Managing diabetes is crucial for improving your quality of life and avoiding long-term complications. Diabetes is a chronic condition that requires careful management. Controlling blood sugar levels is possible through proper nutrition, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes. In this article, we will cover the main points you need to pay attention to in diabetes management.
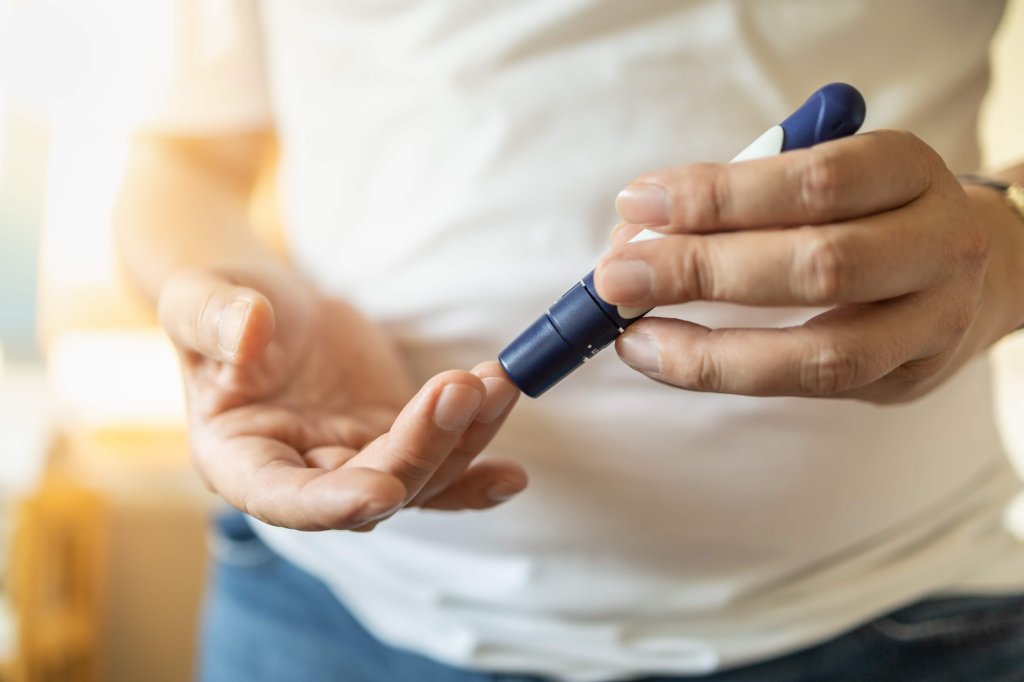
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential in diabetes management. Blood sugar monitoring is one of the most critical components of diabetes treatment and helps keep diabetes under control. Here’s what to keep in mind:
Regular Measurement: Check your blood sugar levels daily. Measuring as often as your doctor recommends is crucial for adhering to your treatment plan.
Target Ranges: Ensure your blood sugar levels stay within the target ranges set by your doctor. These ranges may vary depending on your type of diabetes and overall health.
Emergency Situations: Learn how to respond if your blood sugar levels become too low or too high. Knowing the signs of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia can be life-saving.
Balanced Nutrition
Nutrition is the most important factor in controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of complications in diabetes management. Here’s what to focus on:
Carbohydrate Counting: Track the amount of carbohydrates you consume. Carbohydrates directly affect blood sugar levels, so controlling their amount is crucial.
High-Fiber Foods: Foods high in fiber help prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar by raising it slowly. Whole grains, vegetables, and fruits are rich in fiber.
Healthy Fats and Proteins: Healthy fats and proteins help stabilize blood sugar and increase feelings of fullness. Olive oil, avocado, fish, chicken, and legumes are among these foods.
Regular Exercise
Exercise is an important part of diabetes management and improves blood sugar control. Regular physical activity increases insulin sensitivity and helps with weight management. Keep the following in mind during exercise:
Regular Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week. Activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming can help regulate blood sugar.
Blood Sugar Monitoring: Check your blood sugar levels before and after exercise. Remember that blood sugar may drop during exercise.
Stretching and Strength Training: Stretching and strength training can increase muscle mass, speed up your metabolism, and be effective in diabetes management.
Medication and Insulin Use
Medications and insulin are vital for keeping blood sugar levels under control in diabetes treatment. Here’s what to consider:
Prescription Medications: Take your prescribed medications regularly. Skipping or altering doses can negatively affect your blood sugar levels.
Insulin Management: If you use insulin, it is crucial to adjust the dosage correctly and administer injections on time. Strictly follow your doctor’s instructions regarding insulin use.
Side Effects: Know the possible side effects of your medications and what to do if they occur.
Regular Doctor Visits
Diabetes management requires constant monitoring, and regular doctor visits are an important part of this process. Here’s what to keep in mind during doctor visits:
HBA1C Test: This test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Regular HBA1C tests can help determine how well your diabetes is controlled.
Eye and Foot Examinations: Regular eye and foot examinations are essential to prevent complications from diabetes. Diabetes can have serious effects, especially on the eyes and feet.
Kidney Function: Diabetes can also affect the kidneys, so it’s important to have your kidney functions checked regularly.
Stress Management
Stress can affect blood sugar levels and make diabetes management more challenging. Here’s what to focus on in stress management:
Relaxation Techniques: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help reduce stress and improve blood sugar control.
Sleep Routine: Adequate and quality sleep reduces stress levels and has a positive impact on overall health. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
Social Support: Family, friends, and diabetes support groups can help with stress management and increase your motivation.
Be Prepared for Emergencies
Being prepared for emergencies is also important in diabetes management. Knowing what to do in emergencies like hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia can be life-saving. Here’s what to consider:
Emergency Kits: Carry emergency kits with items like glucose tablets that you can use quickly in case of hypoglycemia.
Emergency Information: Carry information about whom to contact in emergencies and share this information with your family.
Education: Learn how to respond to diabetes-related emergencies and educate those around you.
Paying attention to these aspects of diabetes management is crucial for maintaining a healthy life. Blood sugar monitoring, balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and regular doctor visits help keep your diabetes under control. Additionally, stress management and being prepared for emergencies are important parts of diabetes management. Properly managing diabetes improves your quality of life and helps you avoid complications in the long term. Take your steps carefully for a healthy life!