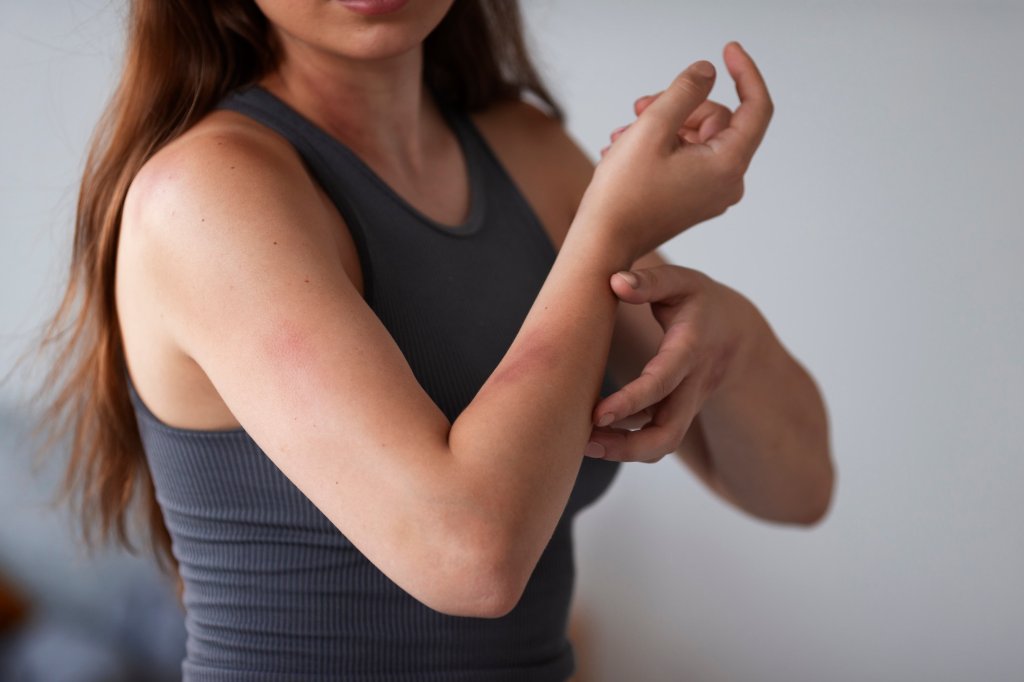
Allergic eczema is a condition that manifests with symptoms such as itching, redness, and swelling on the skin, significantly affecting the quality of life. To understand the underlying causes of this condition and to determine the appropriate treatment method, an allergic eczema test, also known as a patch test, is frequently used. So, what is this test, how is it done, and who needs it?
What Is an Allergic Eczema Test (Patch Test)?
An allergic eczema test, or patch test, is a diagnostic method used to identify substances that cause allergic reactions on the skin. Eczema often results from the skin's reaction to an allergen, and identifying this allergen is crucial in the treatment process. The patch test is conducted by applying special strips containing various allergens to the skin and observing the skin's reaction to these substances.
How Is an Allergic Eczema Test Done?
The patch test is a simple and painless procedure usually carried out in the following steps:
Preparation: A few days before the test, the patient may need to stop taking certain medications, especially antihistamines, as they can affect the test results. This should be done as advised by the doctor.
Selection of Allergens: The dermatologist selects the allergens to be used in the test based on the patient's eczema symptoms. These allergens can include chemicals, metals, fragrances, cosmetics, or other common allergens.
Application of the Patch: The selected allergens are placed on small strips, which are then applied to the patient's back. These strips remain on the skin for 48 hours, during which time the patient should avoid bathing.
Evaluation of Results: After 48 hours, the strips are removed, and the dermatologist checks for any reactions on the skin. If redness, swelling, or itching occurs, it indicates that the patient is allergic to that particular substance.
When Is an Allergic Eczema Test Necessary?
The patch test is recommended, especially in chronic eczema cases where the cause cannot be precisely determined. When eczema recurs persistently and does not respond to treatment, identifying the allergens becomes crucial in the treatment process. Additionally, if the patient has noticed skin issues after coming into contact with certain substances known to trigger eczema, the patch test can confirm these allergens.
Benefits of the Patch Test
The patch test is a reliable method for identifying the causes of allergic eczema. Its most significant advantage is its ability to detect specific substances that cause allergic reactions on the skin. This allows patients to avoid eczema triggers, leading to healthier skin. Furthermore, the results obtained from the patch test are crucial in guiding the treatment process. With an accurate diagnosis, a suitable treatment plan can be prepared, which helps in controlling eczema.
Post-Test Care for the Patch Test
After the patch test, the skin may experience mild redness or itching, which is typically temporary and a natural response to the tested allergens. However, if a severe reaction occurs after the test, it is important to contact the dermatologist. Based on the test results, the doctor will advise the patient on which substances to avoid and may provide recommendations for skin care as needed.